March 25, 2024
Economic Analysis Finds Every $1 of NIH Research Funding
Generates $2.46 in Economic Activity
WASHINGTON, DC — March 25, 2024 — Research funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) generated $92.89 billion in new economic activity nationwide last year — or $2.46 of economic activity for every $1 of research funding, according to a report from United for Medical Research (UMR). NIH’s Role in Sustaining the U.S. Economy, published annually by UMR, also found that the $37.81 billion awarded to researchers in the 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia in Fiscal Year 2023 supported 412,041 jobs.
“Every research dollar that leaves NIH does double duty by supporting life-changing research and by generating jobs and economic activity that support local economies across the United States,” said Caitlin Leach, UMR President.
“Increases to the NIH budget over the past eight years have been instrumental in making progress against our most vexing diseases and maintaining America’s leadership in biomedical research. Failure to continue to invest robustly in medical research through the NIH will immediately reduce funding for research and its benefit to local economies. However, the longer-term consequences of a shrinking NIH budget will be far greater, with a significant negative impact on biomedical innovation, public health and the U.S. economy,” Leach added. ”
More than 80 percent of the NIH budget is awarded in grants each year to researchers at academic institutions, non-profits and businesses. That funding supports employment and the purchase of research-related goods, services and materials. The income generated from these jobs and purchases cycles through the economy to produce new economic activity.
Since Fiscal Year 2015, the NIH budget has grown by more than $17 billion thanks to bipartisan congressional support and a commitment to making medical research a critical national priority. The annual increases to the NIH budget in fiscal years 2016-2023 have enabled the NIH to fund a greater number of grants each year. This momentum was essential and helped the NIH catch up from a long period of flat funding and begin to restore lost purchasing power. Continued robust funding for the NIH is essential to continuing this progress.
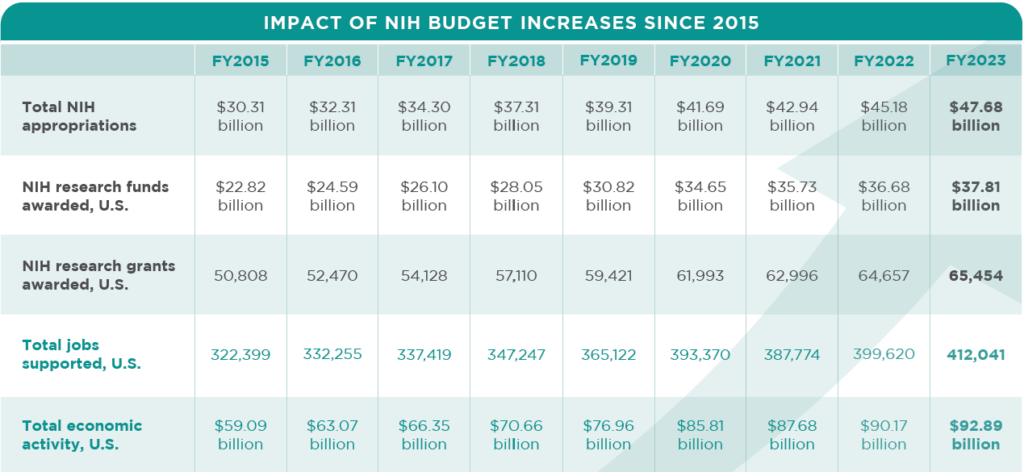
UMR’s analysis of the employment and economic activity attributable to NIH extramural research spending in the 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia, relies on the RIMS II model maintained by the Bureau of Economic Analysis, part of the U.S. Department of Commerce. While RIMS parameters are updated each year, they lag by two years. Therefore this 2023 update and fiscal years 2022 and 2021 were calculated with the latest available RIMS parameters, which are for 2021. Updated calculations for fiscal years 2015-2020 use estimates of annual RIMS parameters where these parameters are interpolated based on published values for 2013 and 2021. The analysis for this 2023 update was performed by Ronald Horst, Ph.D., Inforum.
Access Economic Report and State Toolkit here.
UMR is a coalition of leading research institutions, patient and health advocates and private industry seeking strong and sustainable increases in funding for the National Institutes of Health in order to save and improve lives, advance innovation and fuel the economy. Learn more at unitedformedicalresearch.org.
